- Eukaryotic cell cycle and DNA replication
- DNA double-strand break repair
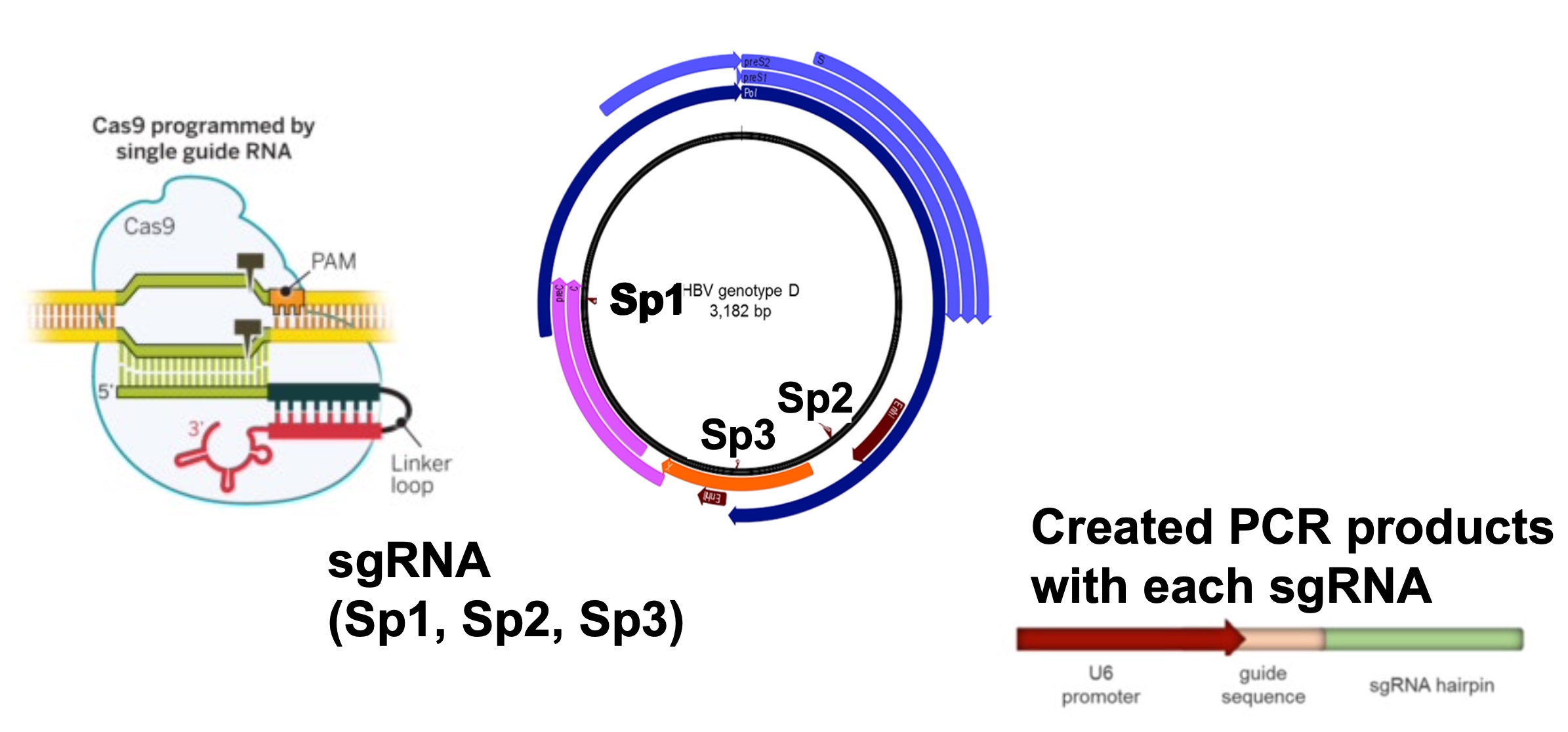
- CRISPR-Cas9 and genome editing
HBV Infects
HBV Structure

HBV Life Cycle

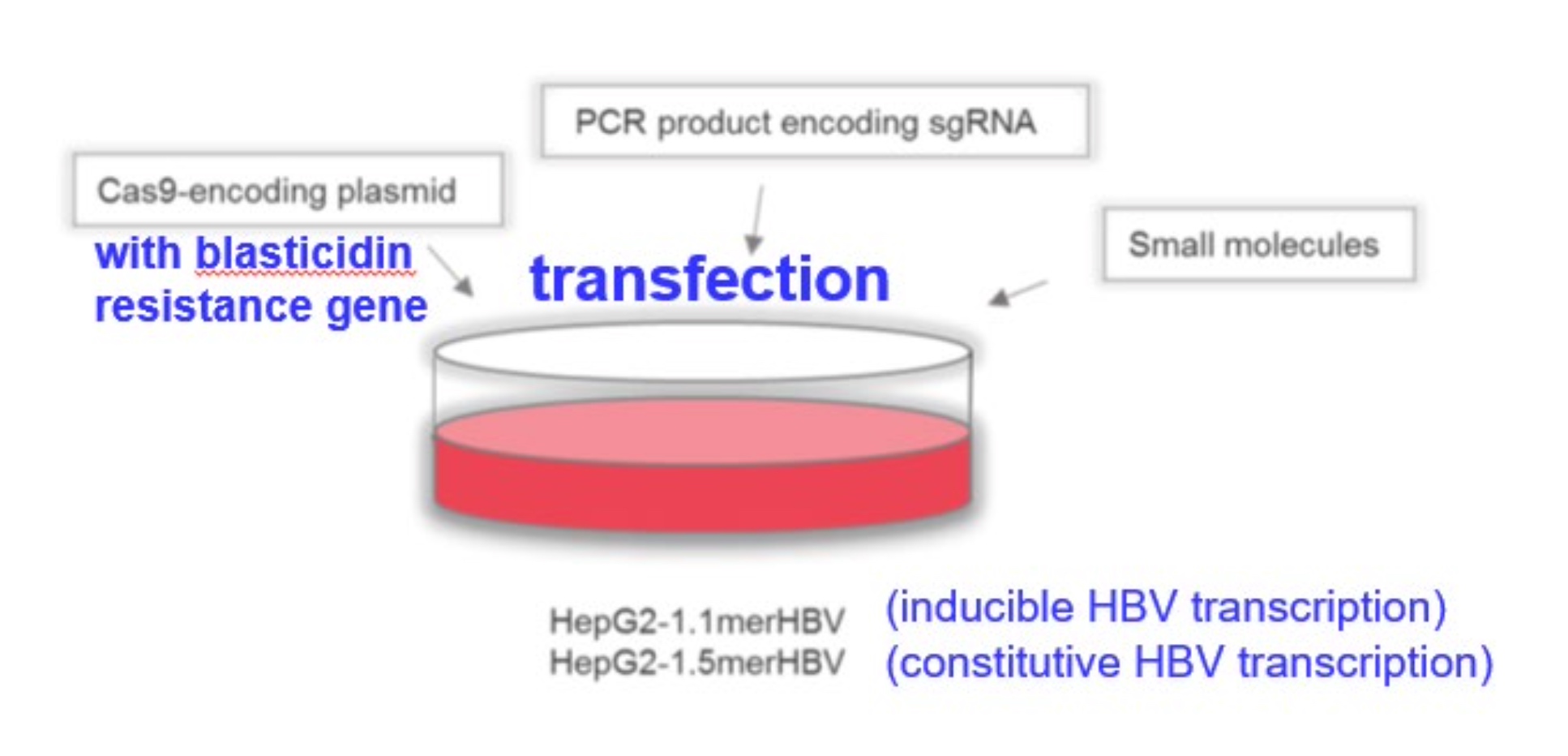
Experimental Methodology
Targeting Proteins Involved in Doubl-strand Break Repair
The variation relative content of two RNA and DNA in CRISPR/Cas9 treated cells after different smal molecules been used.
q-PCR
Relative levels of HBV cccDNA either remained at the level of mock control when using Sp1 sgRNA or were significantly higher compared to DMSO-treated group .
Summary
- CRISPR-Cas9 using sgRNAs targeting HBV effectively decreases cccDNA levels
- Inhibition of the end joining component DNA-PKcs
does not make Cas9 targeting of cccDNA more efficient - There are more on-target deletions with DNA-PKcs inhibition
